Email Verification Trends: How Websites Are Adapting to Combat Spam

The evolving battleground between legitimate websites and spam operations
The Verification Arms Race: A Digital Ecosystem Under Pressure
The relationship between websites and their users exists in a delicate balance. On one side, platforms need to verify legitimate users while deterring automated systems and spam operations. On the other, users seek frictionless experiences without cumbersome security hurdles. This tension has created an ongoing technological arms race that continues to reshape how we interact with digital services.
Consider these revealing statistics about our current digital landscape:
- Over 85% of global email traffic in early 2025 consists of spam, phishing attempts, and automated messages
- Businesses lose approximately $20.5 billion annually to spam-related productivity decreases and technical countermeasures
- The average internet user encounters 13 different verification systems weekly
- 67% of users have abandoned a signup process due to overly complex verification requirements
- Data breaches exposing email addresses increased 34% between 2023 and 2025
These realities have forced websites to continuously evolve their verification approaches, creating a fascinating progression of technologies and methodologies that balance security with usability.
The Evolution of Email Verification: From Simple to Sophisticated
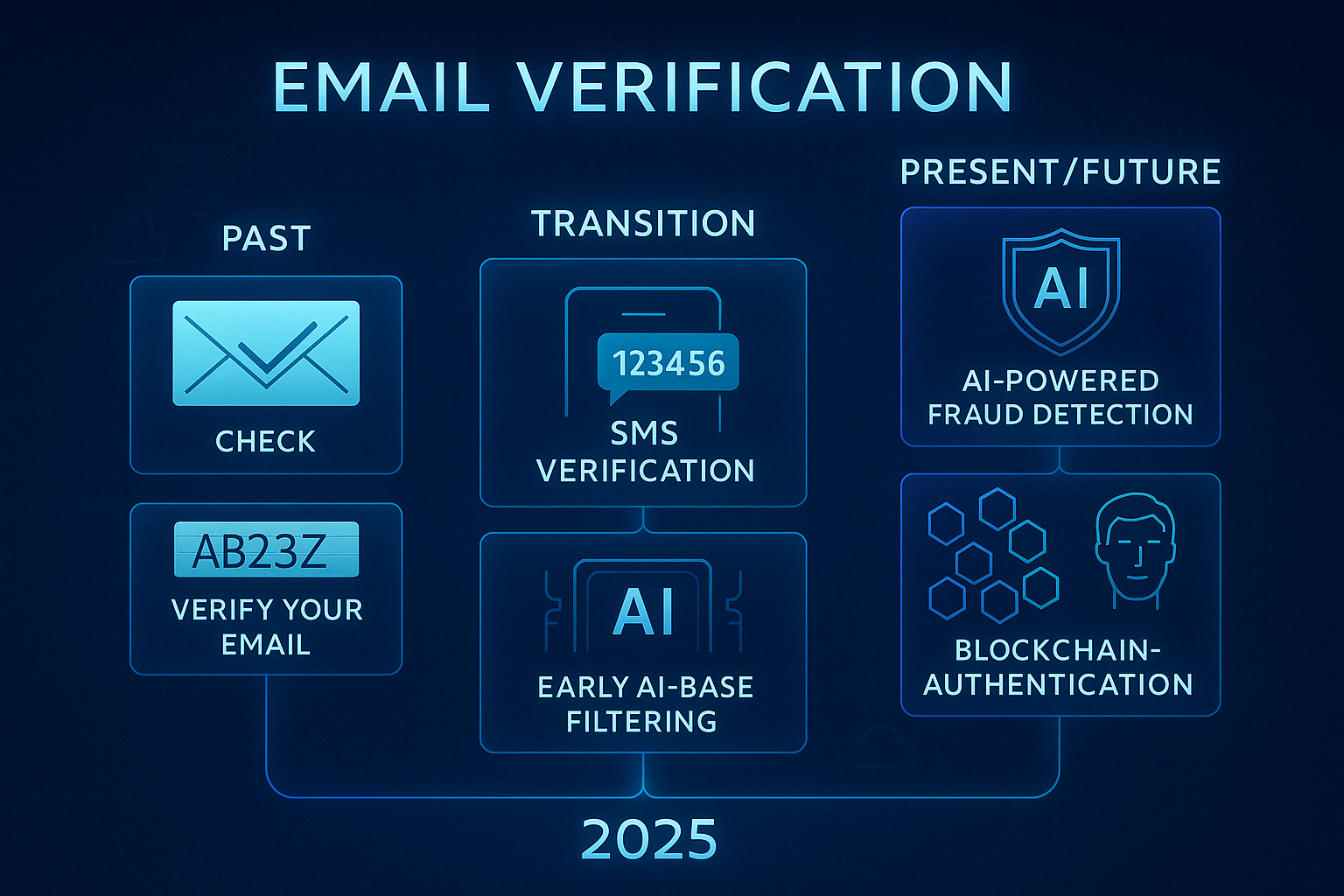
The progression of verification technologies over the past decade
Email verification has undergone remarkable transformation since the early days of the internet. Understanding this evolution provides valuable context for appreciating current approaches and anticipating future developments.
The Simple Confirmation Era (Early Internet)
The earliest verification systems operated on a straightforward premise: if you could receive an email at an address, you must have legitimate access to that address. This approach featured:
- Basic confirmation links sent to provided email addresses
- Minimal protection against automated systems
- No verification of the email's legitimacy beyond deliverability
- Limited ability to prevent disposable email usage
While functionally sound for its era, this approach quickly proved insufficient as spam operations grew in sophistication and scale.
The Challenge-Response Period (2010-2018)
As automated systems became more advanced, websites implemented additional layers of verification to distinguish between human and machine users:
- Text-based CAPTCHAs requiring interpretation of distorted characters
- Image recognition challenges (selecting specific objects from grids)
- Basic behavioral analysis (mouse movements, typing patterns)
- Email domain filtering to block known temporary email services
These methods significantly increased security but often at the expense of user experience, creating frustration and abandonment during registration processes.
The Invisible Authentication Wave (2018-2023)
Recognizing the friction caused by explicit challenges, verification systems began shifting toward less intrusive methods:
- Background behavioral analysis (how users navigate sites)
- Device fingerprinting to identify suspicious patterns
- Reputation scoring based on IP addresses and browsing history
- Sophisticated temporary email detection using pattern recognition
- Risk-based authentication applying different levels of scrutiny based on perceived threat levels
These approaches improved user experience while maintaining reasonable security, though privacy concerns emerged regarding the data collection required for these systems.
The Intelligent Verification Era (2023-Present)
Today's most advanced systems employ multi-layered approaches that adapt dynamically to perceived threat levels:
- AI-powered risk assessment evaluating numerous signals simultaneously
- Contextual authentication adjusting verification requirements based on specific actions
- Federated identity systems allowing verification through established trusted providers
- Passive biometric analysis (typing patterns, device handling)
- Sophisticated email reputation scoring systems
This current generation of verification technologies represents a significant advancement in balancing security with usability, though the arms race continues as both legitimate services and malicious actors refine their approaches.
Current Battlegrounds: How Websites Fight Unwanted Registrations

The multi-faceted approach to verification in today's digital landscape
Modern websites employ diverse strategies to verify legitimate users while deterring unwanted registrations. These approaches typically fall into several distinct categories, each with unique strengths and limitations.
Behavioral Analysis Systems
Rather than explicit challenges, many platforms now analyze how users interact with their interfaces:
- Mouse movement patterns that distinguish humans from automated systems
- Typing rhythm analysis that identifies natural human inconsistencies
- Page interaction behaviors (scrolling, hesitation, exploration)
- Session timing patterns that flag suspiciously efficient completion
These systems operate invisibly, creating no friction for legitimate users while effectively identifying many automated attempts. However, they require significant data collection and processing capabilities, raising privacy considerations explored in our article on the privacy paradox.
Advanced CAPTCHA Alternatives
Traditional CAPTCHAs have evolved into more sophisticated systems that balance security with usability:
- Single-click verification using background risk analysis
- Game-like challenges that feel engaging rather than obstructive
- Accessibility-focused alternatives for users with disabilities
- Contextual challenges that appear only when suspicious activity is detected
These modern approaches significantly reduce user friction while maintaining effective protection against automated systems. For users concerned about privacy during these verification processes, temporary email services provide an additional layer of protection.
Email Reputation Systems
Many platforms now evaluate the reputation and characteristics of email addresses themselves:
- Domain age and reputation scoring
- Historical behavior patterns associated with the email provider
- Syntax analysis to identify algorithmically generated addresses
- Cross-reference checking against known legitimate email patterns
These systems effectively identify many suspicious registrations without creating additional user steps, though they sometimes incorrectly flag legitimate but unusual email addresses.
Multi-Factor Authentication Deployment
For sensitive operations, many sites now require verification through multiple channels:
- SMS verification codes sent to mobile devices
- Authentication app integration (Google Authenticator, Authy)
- Physical security key support (YubiKey, Titan)
- Biometric verification through device capabilities
While highly secure, these approaches introduce additional friction and may exclude users without access to required secondary devices. Our article on two-factor authentication and temporary emails explores this relationship in depth.
AI-Powered Fraud Detection
The most sophisticated platforms employ machine learning systems to identify suspicious patterns:
- Natural language processing to detect unusual communication patterns
- Anomaly detection identifying behavior outside established norms
- Predictive modeling that anticipates likely fraudulent approaches
- Continuous learning systems that adapt to emerging threats
These AI-driven approaches represent the cutting edge of verification technology, though they require significant computational resources and carefully designed oversight to prevent algorithmic bias. For more on how AI is transforming email security, see our article on AI email security and machine learning.
The Temporary Email Conundrum: Legitimate Tool or Security Threat?

The nuanced role of disposable email services in the verification ecosystem
Temporary email services like 15MinMail occupy a fascinating position in the verification ecosystem. From different perspectives, they represent either a privacy-protecting tool for legitimate users or a security vulnerability enabling spam operations.
The Website Perspective
From a platform's viewpoint, temporary email services present several challenges:
- They potentially allow users to circumvent communication channels
- They can enable creation of multiple accounts by the same user
- They may reduce the long-term value of user databases
- They can complicate account recovery processes
These concerns have led many websites to implement specific countermeasures against temporary email services, from simple domain blacklisting to sophisticated pattern recognition systems.
The User Perspective
From the user's perspective, temporary email services offer significant benefits:
- Protection against data breaches affecting service providers
- Reduction in unwanted marketing communications
- Prevention of cross-site tracking through email identifiers
- Ability to evaluate services before committing personal information
These advantages make temporary email services valuable tools for privacy-conscious users practicing good digital hygiene in an era of increasing data collection.
Finding Balance: The Emerging Compromise
Increasingly, a nuanced middle ground is emerging that acknowledges legitimate uses for temporary email services:
- Tiered access systems allowing limited functionality with unverified emails
- Contextual policies applying stricter verification only for sensitive operations
- Transparent communication about why persistent email addresses are required for specific functions
- Focus on demonstrating value before requiring permanent contact information
This balanced approach recognizes that fighting temporary email services creates an endless technological arms race, while accommodating their legitimate uses can actually improve overall user experience and trust.
The User Experience Impact: When Security Becomes Self-Defeating

The critical balance between security measures and user satisfaction
The verification methods websites choose significantly impact user experience, conversion rates, and ultimately business success. Research consistently demonstrates that excessive friction during registration processes directly correlates with user abandonment.
The Abandonment Problem
Studies reveal concerning patterns regarding verification friction:
- 27% of users abandon shopping carts when forced to create accounts
- 86% of users report negative perceptions of websites with cumbersome verification
- Mobile users are 37% more likely to abandon complex verification processes
- Each additional verification step reduces conversion rates by approximately 10%
These statistics highlight how overzealous security measures can become self-defeating by driving away legitimate users—the very people websites aim to attract.
Psychological Factors in Verification
User response to verification systems involves complex psychological factors:
- Perceived justification: Users accept friction that appears proportional to the security required
- Transparency: Clear explanations about why verification is necessary increase compliance
- Agency: Giving users choices between verification methods improves satisfaction
- Immediate value: Users tolerate more friction when they perceive immediate benefit
Understanding these psychological elements allows websites to design verification systems that feel reasonable rather than arbitrary to users.
Progressive Security Models
Leading platforms now implement progressive approaches to verification:
- Basic access with minimal verification
- Increased verification requirements only when accessing sensitive functions
- Clear communication about security/convenience tradeoffs
- User control over security levels with transparent consequences
These models acknowledge that verification isn't binary but exists on a spectrum appropriate to different contexts and risk levels. For users navigating these systems, temporary email services provide valuable flexibility during initial exploration phases.
Industry-Specific Approaches: Contextual Verification Strategies
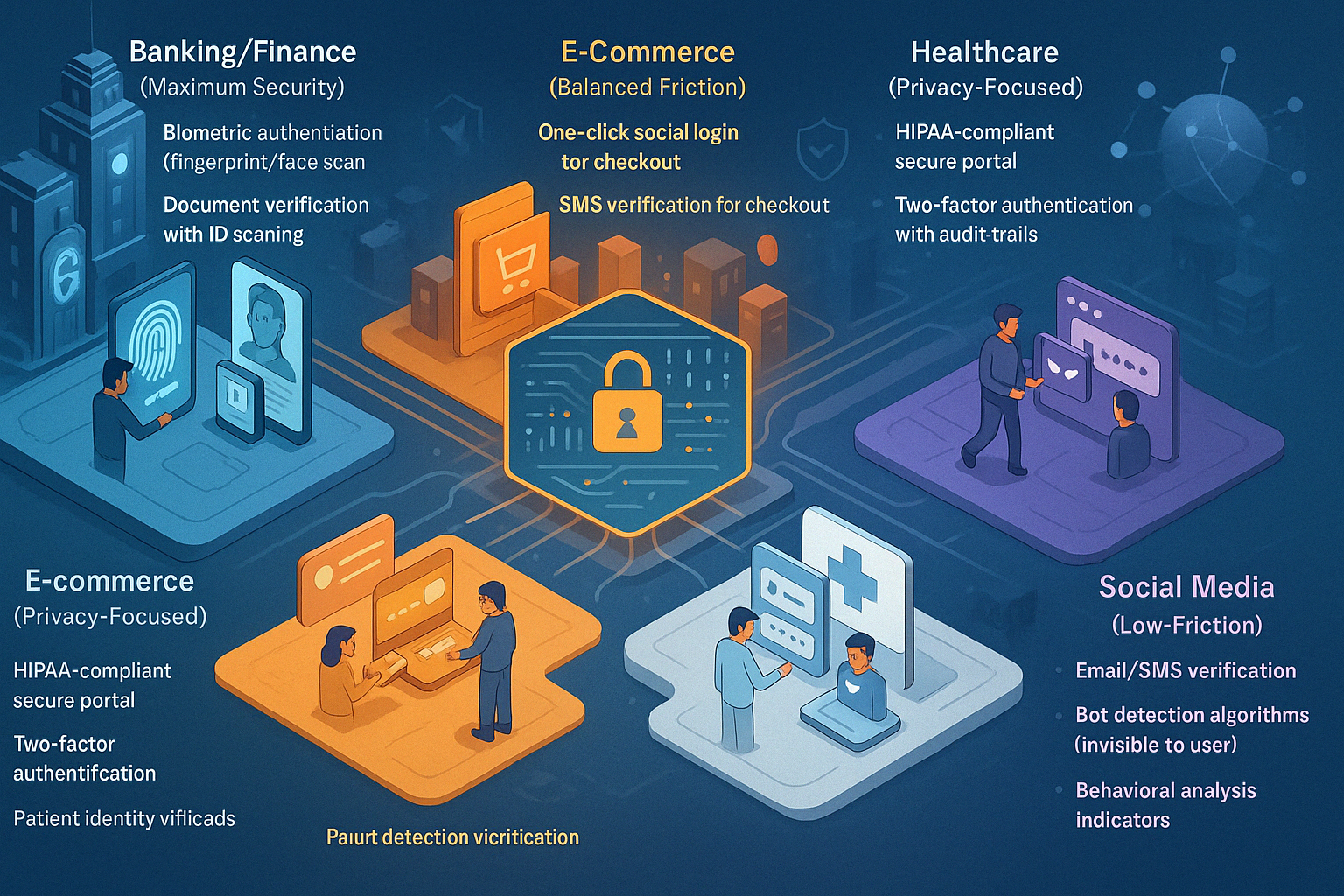
How different sectors balance security needs with user experience
Verification requirements and approaches vary significantly across industries based on their specific security needs, regulatory requirements, and user expectations.
E-Commerce and Retail
Online shopping platforms typically prioritize conversion rates while maintaining basic security:
- Guest checkout options requiring minimal verification
- Account creation incentivized through benefits rather than requirements
- Fraud detection focused on payment processes rather than identity
- Email verification primarily for order confirmation rather than security
This approach acknowledges that excessive friction directly impacts revenue in highly competitive markets. For shoppers concerned about marketing emails following purchases, our guide to smart shopping with temporary email offers valuable strategies.
Financial Services
Banking and financial platforms implement the strictest verification due to regulatory requirements and security stakes:
- Multi-layered identity verification including documentary evidence
- Biometric authentication for sensitive transactions
- Behavioral analysis to detect account takeover attempts
- Continuous authentication throughout user sessions
These rigorous approaches reflect both regulatory requirements and the significant consequences of security breaches in financial contexts.
Social Media Platforms
Social networks balance growth incentives with integrity concerns:
- Streamlined initial verification to encourage signups
- Progressive identity confirmation for expanded privileges
- Sophisticated bot detection systems focusing on behavior patterns
- Community-based verification through connection patterns
This approach allows platforms to grow rapidly while implementing more rigorous verification for accounts seeking expanded reach or capabilities. For those researching platforms before committing, our article on social media research with temporary email provides useful guidance.
Content Subscription Services
Media and content platforms focus on preventing credential sharing while minimizing friction:
- Device fingerprinting to identify access patterns
- Location-based verification for unusual login locations
- Periodic reverification for continued access
- IP analysis to detect multiple simultaneous access points
These methods target specific abuse patterns rather than implementing blanket high-friction verification, acknowledging that excessive barriers reduce conversion to paid subscriptions.
The Privacy Dimension: Data Collection in Verification Systems

The data collection implications of modern verification approaches
Advanced verification systems often require extensive data collection, creating tension between security needs and privacy considerations. This dimension has become increasingly important as users grow more aware of data collection practices and their implications.
The Data Footprint of Verification
Modern verification systems may collect and analyze:
- Device information (browser type, operating system, screen resolution)
- Network details (IP address, connection type, service provider)
- Behavioral patterns (typing rhythm, mouse movements, interaction timing)
- Historical usage patterns across multiple sessions
- Location data and movement patterns
This extensive data collection enables sophisticated security but raises legitimate privacy concerns about surveillance and profiling. For those concerned about these practices, temporary email services provide one layer of protection against persistent tracking.
Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance
Verification systems must navigate complex privacy regulations that vary by region:
- GDPR in Europe requiring explicit consent and data minimization
- CCPA in California establishing transparency and opt-out rights
- LGPD in Brazil implementing comprehensive data protection requirements
- Industry-specific regulations in healthcare, finance, and education
These frameworks increasingly require verification systems to balance security needs with privacy rights, forcing innovation in privacy-preserving verification approaches.
Privacy-Preserving Verification Techniques
Emerging approaches aim to verify users while minimizing unnecessary data collection:
- Zero-knowledge proofs verifying attributes without revealing underlying data
- Federated identity systems keeping personal data with trusted providers
- Local processing performing verification calculations on user devices
- Differential privacy adding controlled noise to collected data
These techniques represent the leading edge of verification technology, aiming to resolve the tension between security and privacy. Our article on email encryption basics explores related privacy-preserving technologies.
The Future Landscape: Emerging Verification Technologies

Emerging approaches that will shape the next generation of verification systems
The verification landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with several emerging technologies poised to reshape how websites distinguish legitimate users from unwanted visitors.
Decentralized Identity Systems
Blockchain-based approaches are creating new possibilities for verification:
- Self-sovereign identity allowing users to control their verification credentials
- Distributed verification reducing reliance on central authorities
- Cryptographic proof systems enabling selective disclosure of information
- Immutable audit trails creating accountability without centralized control
These approaches potentially transform the verification paradigm from organization-centric to user-centric models. Our article on Web3 and decentralized email explores related concepts.
Passive Biometric Systems
Advanced biometric approaches are moving beyond explicit scans to passive observation:
- Typing pattern recognition identifying users through keyboard dynamics
- Device handling signatures based on accelerometer and gyroscope data
- Interaction behavior profiles establishing unique user patterns
- Voice pattern analysis during normal system interaction
These methods provide strong identification without requiring specific user actions, though they raise significant privacy considerations that must be carefully addressed.
Contextual Intelligence Networks
Collaborative systems are emerging to share verification insights across platforms:
- Reputation scoring systems spanning multiple services
- Shared signal networks identifying suspicious patterns across websites
- Collaborative filtering of known malicious indicators
- Federated learning improving verification without sharing raw data
These collaborative approaches significantly enhance verification effectiveness while potentially reducing the data collection burden on individual services.
Quantum-Resistant Authentication
As quantum computing advances, new verification approaches are being developed to maintain security:
- Lattice-based cryptography resistant to quantum attacks
- Hash-based signature schemes maintaining integrity in post-quantum environments
- Multivariate polynomial cryptography creating verification challenges resistant to quantum solving
- Code-based cryptographic systems using error-correcting codes
These forward-looking approaches aim to ensure verification systems remain secure even as computational capabilities advance dramatically.
Balancing Act: Best Practices for Modern Verification

Strategies for effective verification that respects user experience and privacy
For websites seeking to implement effective verification while maintaining positive user experiences, several best practices have emerged from industry leaders:
Proportional Security Implementation
Effective verification systems match security levels to actual risk:
- Minimal friction for basic access and browsing
- Progressive verification increasing with sensitive actions
- Risk-based assessment applying stricter verification only when suspicious patterns emerge
- Clear communication about why specific verification is required
This proportional approach prevents the common mistake of applying high-security verification universally, which creates unnecessary friction for low-risk interactions.
Transparent Communication
Users accept verification more readily when they understand its purpose:
- Clear explanations about why verification is necessary
- Transparent descriptions of what data is collected and how it's used
- Straightforward language avoiding technical jargon
- Visible security benefits highlighting how verification protects users
This transparency transforms verification from an arbitrary obstacle to a valuable security measure in users' perception.
Multiple Verification Pathways
Providing options accommodates different user preferences and capabilities:
- Alternative verification methods for users with different devices
- Accessibility-focused options for users with disabilities
- Backup verification pathways when primary methods fail
- Choice between convenience and security levels where appropriate
These options acknowledge user diversity while maintaining security standards. For users navigating these systems, our guide on protecting accounts offers valuable strategies.
Continuous Improvement Through Analytics
Leading verification systems continuously refine their approaches:
- Abandonment analysis identifying where users leave verification processes
- A/B testing of different verification approaches
- User feedback collection about verification experiences
- Conversion impact assessment measuring business effects
This data-driven approach ensures verification systems evolve based on actual user behavior rather than theoretical security models.
The User's Perspective: Navigating Verification Systems
Practical approaches for users managing diverse verification requirements
While websites work to improve verification systems, users can employ several strategies to navigate the current landscape effectively:
Strategic Email Management
Thoughtful email usage helps manage verification efficiently:
- Using temporary email services for initial exploration of new platforms
- Creating purpose-specific permanent emails for different types of services
- Employing plus addressing (username+service@domain.com) for filtering and tracking
- Regularly auditing which services have your email addresses
These approaches provide control over communication channels while working within verification requirements. Our article on protecting your primary inbox offers additional strategies.
Security-Conscious Verification Choices
When verification options exist, selecting appropriate methods enhances security:
- Preferring authenticator apps over SMS for two-factor authentication
- Using hardware security keys for highly sensitive accounts
- Selecting biometric options when device security is strong
- Avoiding SMS verification on publicly listed phone numbers
These choices maximize the security benefits of verification while minimizing vulnerability to common attack vectors.
Privacy-Preserving Approaches
Users can minimize unnecessary data exposure during verification:
- Reviewing privacy policies before providing verification information
- Using privacy-focused browsers during verification processes
- Selecting federated identity providers with strong privacy practices
- Providing only information specifically required for verification
These practices help maintain privacy while still completing necessary verification steps. Our guide on avoiding spam provides complementary strategies.
Friction-Benefit Analysis
Evaluating whether verification friction justifies service benefits:
- Considering whether the service warrants sharing persistent contact information
- Evaluating privacy policies before completing high-friction verification
- Seeking alternatives when verification requirements seem disproportionate
- Providing feedback when verification creates unnecessary obstacles
This thoughtful approach ensures users invest verification effort proportionally to the value received.
Conclusion: The Verification Horizon
Email verification represents a fascinating microcosm of the broader digital security landscape—a continuous evolution of measures and countermeasures as both protective systems and threat actors advance their capabilities. The most successful approaches increasingly recognize that verification isn't simply a technical challenge but a human one, requiring careful balance between security, privacy, and user experience.
As we look toward the future, several trends appear likely to shape the next generation of verification systems:
- Increasing personalization of verification based on individual user patterns and risk profiles
- Greater user control over identity information through decentralized systems
- More sophisticated privacy-preserving verification techniques minimizing unnecessary data collection
- Continued refinement of invisible verification methods that maintain security without creating friction
For users navigating this evolving landscape, services like 15MinMail provide valuable tools for maintaining privacy and control while interacting with diverse verification requirements. By understanding both the legitimate security needs of websites and the privacy concerns of users, we can work toward verification systems that effectively protect digital spaces while respecting individual rights and experiences.
Whether you're a website developer implementing verification systems or a user navigating them, approaching verification as a balanced ecosystem rather than an adversarial battlefield creates opportunities for solutions that serve everyone's legitimate interests.
This article was last updated on April 19, 2025, to reflect the most current verification technologies and practices.